10 Tips to Introduce Reading to a Young Child Who Is Blind or Visually Impaired
 One of the first and most important things to remember when introducing books and literacy experiences to a young child with a visual impairment is that the child is a child first. While there are certain tips and techniques that will make reading more meaningful and pleasurable for children who are blind or visually impaired, many of the same principles apply to ALL children. Sharing quiet time together with a family member, teacher or other special person enjoying stories that are funny or interesting is something that all of us love, regardless of our age or the amount of vision we have.
One of the first and most important things to remember when introducing books and literacy experiences to a young child with a visual impairment is that the child is a child first. While there are certain tips and techniques that will make reading more meaningful and pleasurable for children who are blind or visually impaired, many of the same principles apply to ALL children. Sharing quiet time together with a family member, teacher or other special person enjoying stories that are funny or interesting is something that all of us love, regardless of our age or the amount of vision we have.1. Share your love of reading by reading aloud with your child every day.
It is important to set aside time each day to read with your child. This does not mean that you have to read a book from cover to cover or make the child listen to each and every page. This means that you show your child that books are something special to be enjoyed and that they can make life more interesting and fun.
2. Choose times and places that are quiet, comfortable and free from distractions
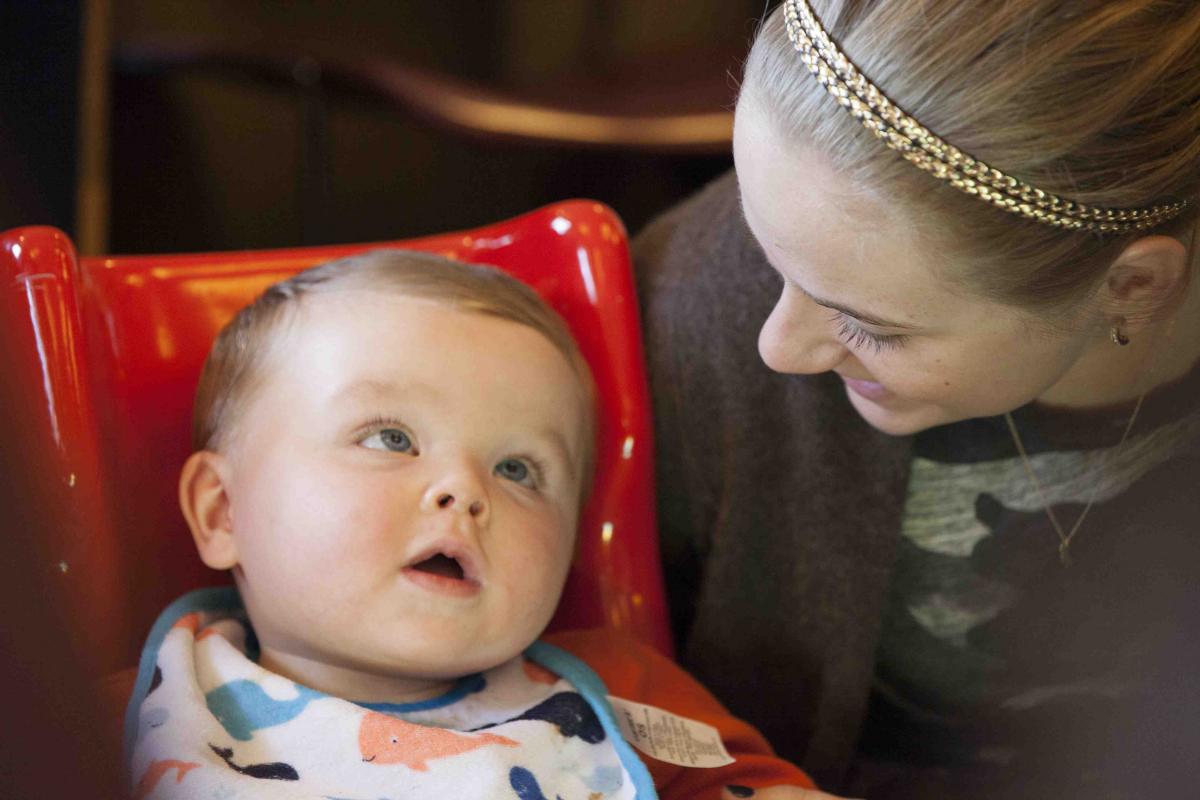 Life is often busy and can be chaotic, especially when juggling schedules and other children. Turn off your cell phone and the TV, sit close to the child, and really focus on exploring books and literacy materials together. Be sure that the child is comfortable, with proper positioning, so that she can focus on you and the story rather than on trying to sit up. This simple act of sharing focused time together will help to create a routine that is special and enjoyable for both you and the child.
Life is often busy and can be chaotic, especially when juggling schedules and other children. Turn off your cell phone and the TV, sit close to the child, and really focus on exploring books and literacy materials together. Be sure that the child is comfortable, with proper positioning, so that she can focus on you and the story rather than on trying to sit up. This simple act of sharing focused time together will help to create a routine that is special and enjoyable for both you and the child.

3. Choose books that relate to the child’s own experience.
Many young children who are blind or visually impaired have limited experience with the world, and if they have additional disabilities or are deafblind this is even more true. Books about rocketships or monsters will have limited meaning to children who don't know these concepts, and it is best to begin with simple books that relate directly to a child's own experience. One favorite that many children enjoy from a young age is Little Rabbit's Bedtime. It includes familiar routines, such as taking a bath and brushing teeth, and real objects can be shown to the child while reading the book (i.e. a real toothbrush and washcloth).
Click here to see how it can be used with real objects.
For older children or children with multiple disabilities Lunch Crunch offers a simple story line where you can use real carrots, crackers, etc. to accompany the story. See this post for more ideas on how to set this up.
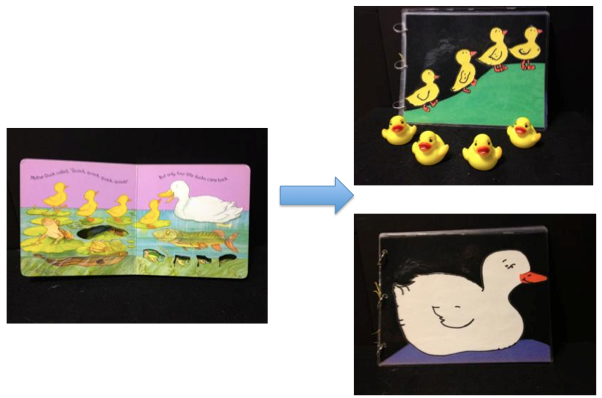
4. Use objects to support the story, in place of illustrations (storyboxes).
 As with the examples above, real objects can be used to illustrate and expand the story. These can help children to identify objects mentioned in the story (e.g. a pair of shoes) or to encourage them to act something out (e.g. brushing hair). Story boxes are collections of items from a given book that are stored together with the book in a convenient way. There are many examples of story boxes on this site.
As with the examples above, real objects can be used to illustrate and expand the story. These can help children to identify objects mentioned in the story (e.g. a pair of shoes) or to encourage them to act something out (e.g. brushing hair). Story boxes are collections of items from a given book that are stored together with the book in a convenient way. There are many examples of story boxes on this site.
5. Add textures or bright colors to call attention to important parts of the page.
The type of adaptation used will depend on the individual child, including the amount of vision they have and the specific vision condition. CVI or Cortical Visual Impairment, for example, often calls for different types of adaptations. In general textures or bright colors can be used to call the child's attention to a certain part of the page or to make the meaning clearer.
See Modifying Books for Students with Multiple Disabilities for more ideas.
6. Use interactive language to make the story more engaging and meaningful.
7. Provide books in braille and/or large print.
Braillable labels or sheets can be created as overlays that can be added to individual pages. There are also many sources of braille books, some of which are free. Work with your child's teacher of students with visual impairments (TVI) to identify sources of books or to find help creating braille books. One parent had the idea of hosting a book making party! Click here to read how she did it.
8. Encourage the child to be actively engaged in the handling of the book.
Invite the child to:
- find the cover
- open the book
- turn the page
- find the "top of the page"
9. Create tactile books with the child, based on their experiences.
Blogger Liam’s mom shares lots of great ideas for creating experience books for your child. Experience books are created by collecting real objects associated with a given experience and making them into a book. Look at her post on How to Create an Experience Book.
10. Store the books and other literacy materials in an accessible place that the child can find.
Designate a shelf or cabinet that the child can locate and reach. Label it with braille and/or a tactile symbol or picture to indicate that this is where to books are kept. Encourage the child to find the shelf and choose a book to look at. Invite her to return the books to the shelf after reading time, so that she will learn about where things are stored and can thereby take a more active role in selecting books and making literacy an active choice in her life.
Most important of all -- Enjoy!



Comments
Visually-Impaired Students (CVI)
Resources for Teacher